Renal Replacement Lipomatosis (RRL) a.k.a Replacement fibrolipomatosis, an extremely rare condition, considered as an advanced form of renal sinus lipomatosis.The latter one is a milder form of the spectrum where the normally present renal sinus fat becomes prominent with ageing, obesity or exogenous steroids. Then again, how extreme can it go?
Renal Replacement Lipomatosis (RRL) is usually associated with infection, long term hydronephrosis, calculi and severe renal parenchymal atrophy. Renal calculous disease along with inflammatory changes are present in ~70% of the cases, and these produced symptoms of flank pain and fever.
The patient is a 60 yr old female patient with non-specific abdominal symptoms.
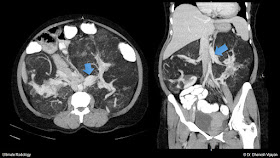
The above image is the non-contrast (plain) CT images which shows diffuse heterogeneous fatty tissue, filling almost the entire abdomen. On further inspection, we can see the fatty tissue is replacing the normal renal parenchyma (orange arrows), and are displacing the retroperitoneal structures like pancreas and duodenum anteriorly. Both kidneys are markedly enlarged, with near complete fatty replacement of the left kidney. Right kidney shows residual parenchyma (green arrow) in lower pole and in the interpolar region (mid-third). A few discrete fatty lesions (blue arrow) are also seen in the residual right renal parenchyma.
Above image shows the mass effect of the enlarged kidneys.
MIP (31mm) image on left shows the bilateral inferiorly oriented renal arteries, residual enhancing parenchyma of right kidney with fatty lesions. On the right, the axial post contrast images show the marked anterior displacement of the ascending colon (blue arrow) and descending colon (orange arrow).
3D VRT image showing the orientation of bilateral main renal arteries.
Delayed MIP images showing contrast excretion into the pelvicalyceal system of both kidneys. Right proximal ureter is marked by the orange arrow.
Delayed MIP axial and coronal images showing the right proximal ureter (orange arrow) and green arrows point to the opacification of pelvicalyceal system. No significant delay in contrast excretion was noted in this patient.
3D VRT of delayed excretory phase showing contrast within the pelvicalyceal system of both kidneys.
As expected renal veins showed moderate dilatation, with left renal vein measuring up to 17mm in diameter.
REFERENCES :
Indian J Nephrol. 2010 Apr; 20(2): 92–93. doi: 10.4103/0971-4065.65303, PMCID: PMC2931141, Renal replacement lipomatosis: A rare type of renal pseudotumor, N. A. Choh, M Jehangir, and S. A. Choh. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2931141/
Setty N, Uma K, Narvekar V N, Desai R S. Bilateral idiopathic replacement lipomatosis of the kidney with posterior mediastinal lipomatosis. Indian J Radiol Imaging [serial online] 2002 [cited 2017 Jun 21];12:251-2. Available from: http://www.ijri.org/text.asp?2002/12/2/251/28457









No comments:
Post a Comment