Thrombi are mainly of three types based on their composition : platelet rich (white) thrombi, red thrombi containing rich fibrin network and RBCs and finally the mixed ones. White thrombi are formed mainly in atherosclerotic plaque ruptures, where as red thrombi are formed in low pressure systems like cardiac or venous systems.
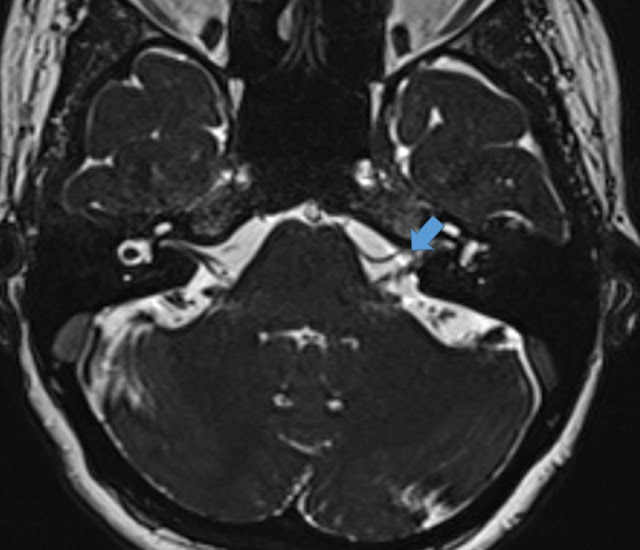
The oxyhemoglobin which gets degraded into de-oxy hemoglobin, methemoglobin and hemosiderin, all have paramagnetic properties and produces susceptibility artifacts in GRE images. This concept is the main core of Susceptibility Vessel Sign.
Teaching Point : GRE SVS is associated with red thrombi and thereby favors a Cardio-Embolic Stroke in most cases. And it also signifies increased chance of subsequent spontaneous recanalization and also increased success rates with fibrinolytic therapy.
Exceptions :
1.SVS –ve cardio-embolic thrombi :
Can occur if MRI was taken before the degradation of Oxy-Hb to Deoxy-Hb (which usually occurs in few hours) OR due missing the section of small thrombus in GRE due to the interslice gap.2.SVS +ve (Large Artery) Atherosclerotic thrombi :
due to the formation of white thrombus initially, can lead to stagnant or reduced flow velocity within the vessel, there by gradually causing increased fibrin and RBC content of thrombus.References :
1. Significance of Susceptibility Vessel Sign on T2*-Weighted Gradient Echo Imaging for Identification of Stroke Subtypes. Kyung-Hee Cho, MD; Jong S. Kim, MD, PhD; Sun U. Kwon, MD, PhD; A-Hyun Cho, MD; Dong-Wha Kang, MD, PhD. Stroke, November 2005.

 What's 'GRE Susceptibility Vessel Sign' ?
What's 'GRE Susceptibility Vessel Sign' ? What's your Diagnosis? : Question 1
What's your Diagnosis? : Question 1